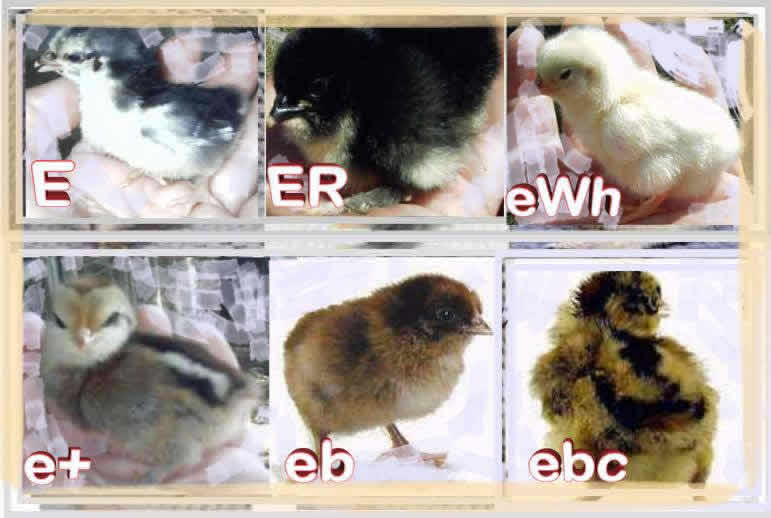
|
The
following gives a basic idea as to the results of pairing Lavender with
Black varieties, Cuckoo with non-barred, Blue with Black & Splash,
White with coloured varieties, Mottled with non-mottled & Silver with
Gold.
* Lavender
(recessive)
eg
Black/Lavender,
Black Mottled/Lavender Mottled, Millefleur/Porcelaine, Silver Millefleur/Silver
Porcelaine, Quail/Lavender Quail, Silver Quail/Lavender Silver Quail breeding
combinations.
Black
+ Lavender = 100% Blacks, all carrying Lavender
Black (carrying Lavender) + Black = All black, 50% carrying
Lavender
Black (carrying Lavender) + Black (carrying Lavender) =
75% Blacks [50% carrying Lavender, 25% pure Blacks], 25% Lavender
Black (carrying Lavender) + Lavender = 50% Blacks [all carrying
Lavender], 50% Lavender
Lavender + Lavender = 100% Lavender
------------------------------------------------------------
* Andalusian
Blue (incomplete dominant)
eg
Black/Blue/Splash, Black Mottle/Blue Mottle, Millefleur/Blue Millefleur/Golden
Neck (Splash Millefleur), Silver Millefleur/ Blue Silver Millefleur, Quail/Blue
Quail/Splash Quail, Silver Quail/Blue Silver Quail, Buff Columbian/Blue
Buff Columbian, Columbian/Blue Columbian breeding combinations.
Andalusian Blue + Black = 50% Blacks, 50% Andalusian
Blue
Andalusian Blue + Andalusian Blue = 25% Blacks, 50% Andalusian
Blue, 25% Splash
Andalusian Blue + Splash = 50% Andalusian Blue, 50% Splash
Splash + Splash = 100% Splash
Splash + Black = 100% Andalusian Blue
-----------------------------------------------------------
* Sex-linked
Gold (recessive) & Sex-linked Silver (dominant)
eg
Millefleur/Silver Millefleur, Quail/Silver Quail, Columbian (Ermine)/Buff
Columbian (Fawn Ermine).
Gold + Gold = all gold
Gold male + Silver female = all gold females, all silver males
(S/s) -carrying gold
Silver
male (S/S) + Gold female = all silvers, all males carrying gold
(S/s)
Silver
(S/s -carrying gold) male + Gold female = of males: 50% Silver [S/s
-all carrying Gold], 50% Gold, of females: 50% Silver, 50% Gold
Silver
(S/s -carrying gold) male + Silver female = of males: 50% Silver -carrying
Gold (S/s), 50% pure Silver (S/S), of females: 50% Silver, 50% Gold
---------------------------------------------------------
*Cuckoo/Barred
(Sex-linked Dominant)
eg
Cuckoo/Black, Lavender Cuckoo/Lavender breeding combinations.
Cuckoo (B/B) + Cuckoo (B/B) = all cuckoo
Black
male + Cuckoo female = females black (non barring), males cuckoo
(B/b) -carrying non-barring/black
Cuckoo
(B/B) male + Black female = all cuckoos, all males (B/b) -carrying
non-barring/ black
Cuckoo
(B/b -carrying non-barring/black) male + Black female =
of males: 50% Cuckoo [B/b -all carrying non-barring/black], 50% Black,
of females: 50% Cuckoo, 50% Black
Cuckoo
(B/b -carrying non-barring/black) male + Cuckoo female =
of males: 50% Cuckoo, (B/b -carrying non-barred/black, 50% pure Cuckoo
(B/B), of females: 50% Cuckoo, 50% Black.
---------------------------------------------------------
* Mottled
(recessive)
eg
Black/Black Mottled, Blue/Blue Mottled, Lavender/Lavender Mottled, Millefleur/Buff
Columbian
Solid + Solid = All solids
Solid
+ Mottled = 100% solids, all carrying mottled
Solid
(carrying Mottled) + Solid = all solid, 50% carrying mottled
Solid (carrying Mottled) + Solid (carrying Mottled) =
75% solids [50% carrying mottled, 25% pure solids], 25% mottled
Solid (carrying Mottled) + Mottled = 50% solids [all carrying
mottled], 50% mottled
Mottled
+ Mottled = 100% Mottled
-------------------------------------------------------
* Recessive
White
eg
Coloured/Recessive White breeding combinations
Coloured + Coloured = all coloured
Coloured + White = 100% coloureds, all carrying white
Coloured (carrying White) + Coloured = all coloured, 50% carrying
white
Coloured (carrying White) + Coloured (carrying White) =
75% coloureds [50% carrying white, 25% pure coloureds], 25% white
Coloured (carrying White) + White = 50% coloureds [all carrying
white], 50% white
White + White = 100% White
 Up to Top
Up to Top

Creating Blue Millefleur variety
1: Blue Buff Columbian
to Millefleur =
½ Buff Columbian, ½ Blue Buff Columbian
Pair F1 Blue Buff Columbian
to Millefleur = ¼
Buff Columbian, ¼ Blue Buff Columbian, ¼ Millefleur, ¼ Blue Millefleur
* If the original Blue Buff
parent is pale buff, then the Millefleur may be too light in ground colour,
ie if possible use a deep Buff
2: Blue
Mottled to Millefleur = ½ Black Mottled, ½ Blue Mottled
Pair F1 Blue Mottled to Millefleur
= ¼ Black Mottled, ¼ Blue Mottled, ¼ Millefleur, ¼ Blue Millefleur
* May have problems with Mottled progeny having gold in neck
hackles, etc, or too much black in neck hackles of Millefleur. The Mottled
with gold in neck hackles are good for pairing back to Millefleur &
Buff Columbian but not necessarily of Mottled show quality.
3:
Buff Columbian to Blue Mottled = ½ Black, ½ Blue
4: Blue Buff Columbian to
Black Mottled = ½ Black, ½ Blue
In 3 & 4, pair Blue F1
back to Millefleur
= 1/8 Black Mottled, 1/8 Blue Mottled,1/8
Blue, 1/8 Black, 1/8 Buff Columbian, 1/8 Blue Buff Columbian, 1/8 Millefleur,
1/8 Blue Millefleur
The best
pairing would be Splash Buff Columbian to Millefleur or Splash Mottled
to Millefleur. This would give all Blue progeny in the F1.
eg Splash Buff Columbian to Millefleur = 100% Blue Buff Columbian, giving you higher numbers to use in next generation &/or
to cull for “type”.
* F1 =
1st generation
There are other pairings that will give you Blue Millefleur,
but smaller percentages.
Pairing Blue Millefleur to Blue Millefleur will give Splash
Millefleur genotype, looking like a Buff Mottled in phenotype. This variety
is called Golden Neck in the USA. The Buff Mottled (Oker Mottled) of Europe
is the Millefleur variety with the Dominant White gene added. They have
a very similar phenotype to the Splash Millefleur (Golden Neck). If you
add the Lavender gene to either the Splash Millefleur or Oker Mottled
(Dominant White Millefleur) you will have the “Cream Mottled”
variety.
 Up to Top
Up to Top
|
![]()

![]() Up
to Top
Up
to Top